Are you waking up to a pillow covered with hair? Or maybe you are bored with your current hairstyle and considering a bold new look?
Whatever your reasons, understanding the various types of hair loss, or alopecia, is essential before making any drastic changes. From the patchy hair loss of alopecia areata to scarring hair loss from cicatricial alopecia, we've got you covered.
While hair loss can be distressing, it's essential to remember that it's not life-threatening. However, it can be a sign of an underlying health issue, such as thyroid problems, lupus, or anemia. If you're noticing excessive hair loss, it is essential to consult a medical professional to rule out any underlying health issues.
6 Common Types of Alopecia
Alopecia comes in various forms. Let's take a closer look at the most common ones.
Androgenetic Alopecia
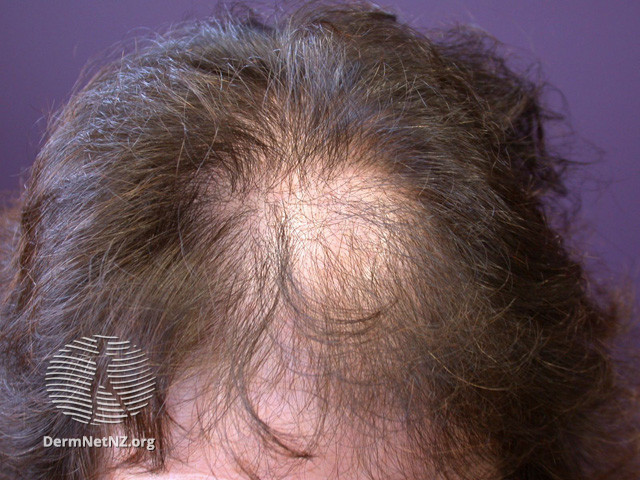

Androgenetic alopecia, widely recognized as male-pattern baldness (male-pattern hair loss, or MPHL) or female-pattern hair loss (FPHL), is the most common type of hair loss. A mix of genetic and hormonal factors causes it.
In men, it often starts with a receding hairline, followed by hair thinning on the crown and temples. In women, it results in general hair thinning on the scalp.
Androgenetic alopecia is a progressive condition, meaning that it worsens over time. It can cause embarrassment and self-consciousness for those affected. While there is no cure for this type of alopecia, there are various treatment options available, including topical medications, oral medications, and hair transplant surgery.
Alopecia Areata

Image courtesy of DermNetNZ
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes patchy hair loss on the scalp and other regions of the body, commonly referred to as "hair falling." The hair loss can occur rapidly or gradually and affects people of all ages and genders. The condition is believed to be triggered by stress or trauma and can be treated with corticosteroids or immunosuppressants.
Alopecia areata significantly affect a person's self-esteem and quality of life. It is essential for those experiencing this type of alopecia to seek medical treatment and support from loved ones.
The most common forms of Alopecia Areata are:
Patchy Alopecia Areata: This is the most common form where one or more round patches of hair loss appear on the scalp or other body areas.
Alopecia Totalis: This is a more advanced form of alopecia areata characterized by total loss of hair on the scalp.
Alopecia Universalis: This is the most severe form of alopecia areata that leads to complete hair loss across the entire body, including the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and pubic hair.
Alopecia Ophiasis: A type of alopecia areata that involves hair loss in a wave pattern that moves from one side of the scalp to the other, typically around the fringe, nape, or sides of the scalp.
Alopecia Areata Barbae: Alopecia Areata Barbae is limited only to the beard area. It may involve one or multiple patches of hair loss in the beard.
Diffuse Alopecia Areata: This type is less common and involves sudden and unexpected hair thinning all over the scalp, not just in certain areas.
Traction Alopecia

Image courtesy of DermNetNZ
Traction alopecia is caused by continuous pulling or tension on the hair, usually due to tight hairstyles such as braids, weaves, or cornrows. Wearing tight hats can also contribute to traction alopecia. Over time, this constant pulling damages the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. This type of alopecia is common in African American women but can affect anyone who wears a tight hairstyle.
Traction alopecia can be prevented by avoiding tight hairstyles and opting for looser, more natural styles. If caught early, the condition can be reversed by stopping the damaging hairstyle and allowing the hair follicles to heal.
Telogen Effluvium

Image courtesy of DermNetNZ
Telogen effluvium is a type of hair loss that happens when physical or emotional stress, hormonal imbalances, or medication disrupts the normal hair growth cycle. This results in premature hair shedding from the scalp, leading to thinning or bald patches.
The good news is, this condition is temporary and the hair will grow back once the underlying cause is treated.
Anagen Effluvium

Image courtesy of DermNetNZ
Anagen effluvium is a type of alopecia that occurs when the hair follicles are damaged during their growth phase, resulting in hair loss. This type of hair loss is most commonly caused by chemotherapy or radiation therapy used to treat cancer.
Anagen effluvium can be a challenging side effect of cancer treatment, but it is essential to remember that it is a temporary condition. Hair will often begin to grow back once treatment is completed.
Cicatricial (Scarring) Alopecia

Image courtesy of DermNetNZ
Cicatricial alopecia, also known as scarring alopecia, is a rare type of hair loss that results from the destruction of hair follicles and their replacement with scar tissue. Various conditions, such as skin diseases, burns, radiation, or infections, can cause the illness.
Cicatricial alopecia can be difficult to treat, as the damage to the hair follicles is often irreversible. Treatment options may include medications to reduce inflammation or surgery to transplant healthy hair follicles to the affected area.
Causes of Alopecia
While the exact causes of alopecia are not entirely clear, several factors can contribute to hair loss.
Genetic Factors
Alopecia can be hereditary, and having a family history of hair loss can increase the risk of developing the condition.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal imbalances due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid problems can cause hair loss in women. In men, hair loss is often linked to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders such as alopecia areata, lupus, or Hashimoto's thyroiditis can cause hair loss by attacking the hair follicles.
Physical Stress and Trauma
Physical stress from surgery, illness, or injury can cause hair loss. Trauma to the hair follicles, such as tight hairstyles or excessive brushing, can also damage the hair and cause it to fall out.
Nutritional Deficiencies
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for healthy hair growth. A deficiency in nutrients such as iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid can lead to hair loss.
Medical Treatments and Medications
Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and certain medications used to treat conditions such as arthritis, depression, and high blood pressure can cause hair loss as a side effect.
Treatment for Alopecia
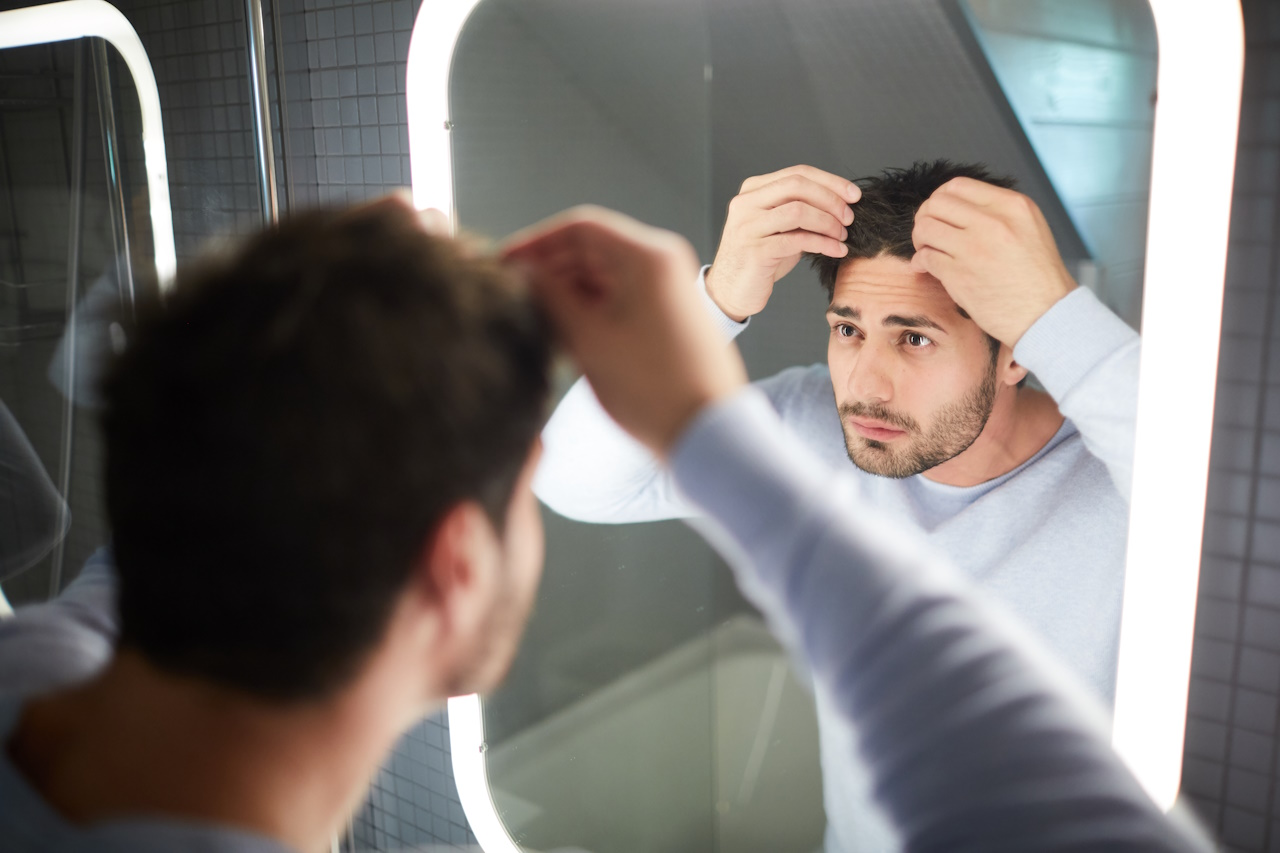

Fortunately, several treatment options are available for alopecia, depending on the underlying cause and severity of hair loss.
Medications

Medications like Minoxidil, Finasteride, or Corticosteroids can help stimulate hair growth and reduce hair loss.
Hair Transplantation
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves transplanting hair follicles from one area of the scalp to another. This can help restore hair growth and improve the appearance of bald patches.
Wigs, Hairpieces, and Hats

Wearing wigs, hairpieces, and hats is a good option for people with severe or permanent hair loss.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet, reducing stress, and avoiding hairstyles that cause tension in the hair, can also help improve hair growth and prevent further hair loss.
Shaving Your Head

Who's to say you need hair at all to look fabulous? Several celebrities, including Dwayne "The Rock" Johnson, Vin Diesel, Jason Statham, Sir Patrick Stewart, and several women like Sinead O'Connor, rock the bald look.

photo via Maxim
So grab a head shaver and rock that bold new look.
Coping with Alopecia
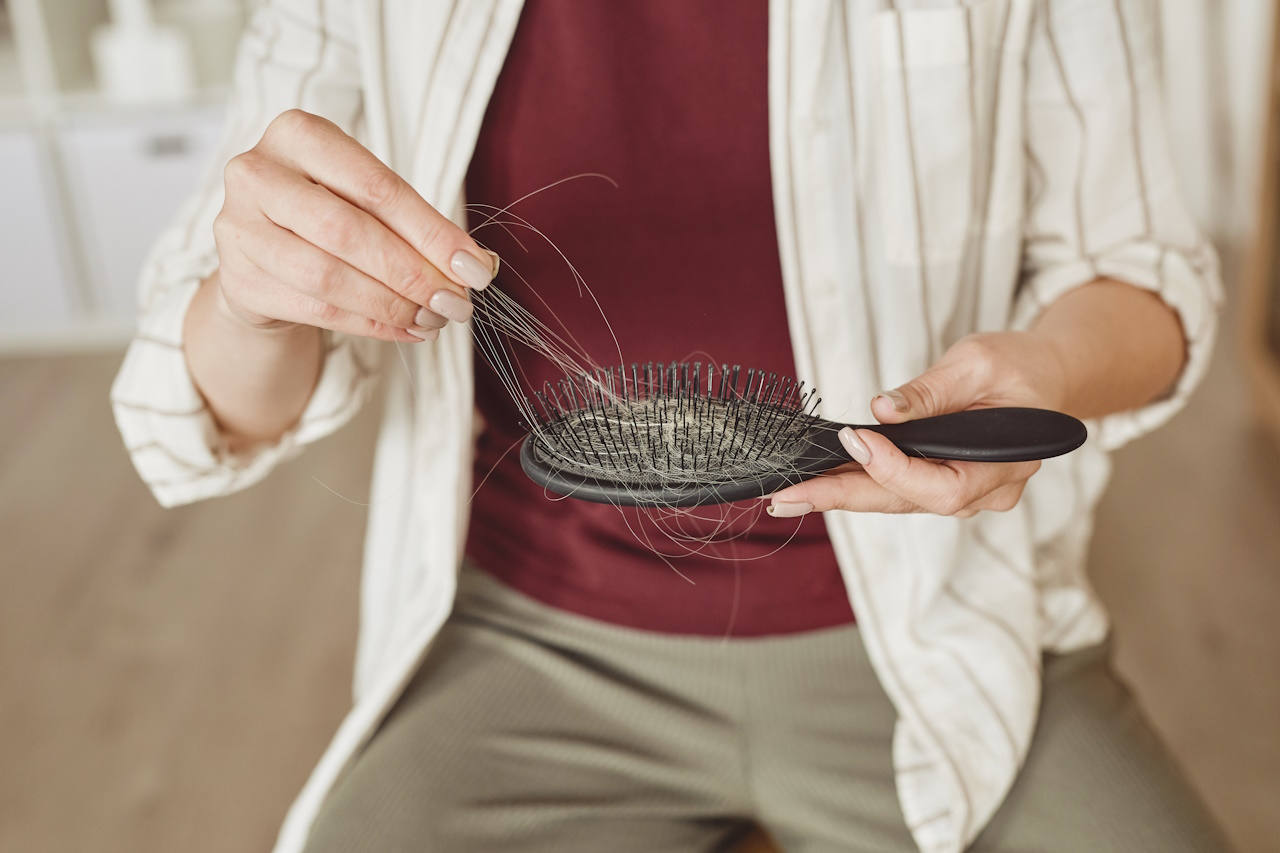

Beyond the physical impact, hair loss can take an emotional toll on affected individuals. Hair is often considered a symbol of beauty and youth; losing it can be a traumatic experience. Individuals may feel embarrassed or ashamed of their appearance, leading to social isolation and anxiety.
Coping with hair loss can be challenging, but it is essential to remember that you are not alone. There are many support groups and online communities available for people with alopecia, where you can connect with others who are going through similar experiences.
Practicing self-care and focusing on your mental and emotional well-being is also essential. Engaging in activities you enjoy and spending time with loved ones can help boost your mood and improve your overall outlook.
Conclusion
Hair loss can be an unpleasant experience, but it is crucial to understand that it is common and can affect anyone. You can make informed decisions about your hair by knowing the various types and causes of alopecia and the available treatments.
So, rock that bald head with pride or try that daring new hairstyle you have always wanted. Remember, hair or no hair, you are beautiful just the way you are!



